 Back Back
Research Article
ScienceAsia 32 (2006): 271-278 |doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2006.32.271
Titrimetric and Modified Spectrophotometric Methods
for the Determination of Amlodipine Besylate Using
Bromate-Bromide Mixture and Two Dyes
Kanakapura Basavaiah,* Umakanthappa Chandrashekar and Paregowda Nagegowda
ABSTRACT: One direct titrimetric method and two indirect spectrophotometric methods for the determination
of amlodipine besylate (ADB) are described. The methods use bromate-bromide mixture and two-dyes,
namely Methyl Orange and Indigo Carmine, as reagents. In titrimetry (Method A), an acidified solution of
ADB is titrated directly with bromate-bromide mixture using methyl orange as an indicator.
Spectrophotometry involves the addition of known excess of bromate-bromide mixture to an acidified
solution of ADB and the determination of the residual bromine based on its ability to bleach the dyes Methyl
Orange (Method B) or Indigo Carmine (Method C) quantitatively. Titrimetry allows the determination of 1-
10 mg of ADB, whereas spectrophotometry is applicable over the concentration ranges of 0.5-3.0 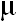 g ml-1 and
1.25-12.50 g ml-1 and
1.25-12.50 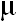 g ml-1 for method B, and method C, respectively. Method B with a calculated molar absorptivity
of 6.56 x 104 l mol-1 cm-1, is the most sensitive method ever developed for ADB. The limits of detection and
quantification are reported for both the spectrophotometric methods. The methods described could usefully
be applied to routine quality control of tablets containing ADB. No interference was observed from common
pharmaceutical adjuvants. Statistical comparison of the results with the reference method shows an excellent
agreement, and indicates no significant difference in accuracy and precision. The reliability of the methods
has been ascertained by recovery studies. g ml-1 for method B, and method C, respectively. Method B with a calculated molar absorptivity
of 6.56 x 104 l mol-1 cm-1, is the most sensitive method ever developed for ADB. The limits of detection and
quantification are reported for both the spectrophotometric methods. The methods described could usefully
be applied to routine quality control of tablets containing ADB. No interference was observed from common
pharmaceutical adjuvants. Statistical comparison of the results with the reference method shows an excellent
agreement, and indicates no significant difference in accuracy and precision. The reliability of the methods
has been ascertained by recovery studies.
Download PDF
Department of Chemistry, University of Mysore, Manasagangotri, Mysore - 570006, Karnataka, India.
* Corresponding author, E-mail: basavaiahk@yahoo.co.in
Received 28 Sep 2005, Accepted 17 Mar 2006
|

