 Back Back
Research Article
ScienceAsia 31 (2005): 207-214 |doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2005.31.207
Determination of Drug Content of Pharmaceuticals
Containing Ranitidine by Titrimetry and
Spectrophotometry in Non-Aqueous Medium
Kanakapura Basavaiaha*, Paregowda Nagegowdaa and Veeraiah Ramakrishnab
ABSTRACT: Three simple, rapid, reliable and cost-effective methods based on titrimetry and spectrophotmetry
in non-aqueous medium are described for the determination of ranitidine in pharmaceuticals. In titrimetry,
the drug dissolved in glacial acetic acid was titrated with acetous perchloric acid with visual and potentiometric
end point detection, crystal violet being used as indicator for visual titration. Spectrophotometry involved
adding different amounts of the drug to a fixed amount of perchloric acid-crystal violet mixture followed by
measurement of absorbance at 570 nm. The absorbance was found to increase linearly with the concentration
of the drug and formed the basis for quantification. The titrimetric methods are applicable over 1-15 mg
range of ranitidine, and in spectrophotometry, calibration graph was linear from 10 to 70 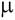 g ml-1. The
apparent molar absorptivity is calculated to be 2.2 x 103 l mol-1 cm-1 and the calculated Sandell sensitivity is
161.7 ng cm-2. The limits of detection and quantification are found to be 1.07 and 3.58 g ml-1. The
apparent molar absorptivity is calculated to be 2.2 x 103 l mol-1 cm-1 and the calculated Sandell sensitivity is
161.7 ng cm-2. The limits of detection and quantification are found to be 1.07 and 3.58 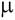 g ml-1, respectively.
The procedures were used to determine ranitidine in pharmaceutical products and the results were found to
be in good agreement with those obtained by the reference method. Associated pharmaceutical materials did
not interfere. The accuracy and reliability of the methods were further ascertained by recovery studies via
standard-addition technique with percent recoveries in the range 96.3 to 102.5 %. g ml-1, respectively.
The procedures were used to determine ranitidine in pharmaceutical products and the results were found to
be in good agreement with those obtained by the reference method. Associated pharmaceutical materials did
not interfere. The accuracy and reliability of the methods were further ascertained by recovery studies via
standard-addition technique with percent recoveries in the range 96.3 to 102.5 %.
Download PDF
a Department of Chemistry, University of Mysore, Manasagangotri, Mysore-570006, India.
b Department of Chemistry, Government College of Pharmacy, Bangalore-560027, India.
* Corresponding author, E-mail: basavaiahk@yahoo.co.in
Received 1 Jun 2004,
Accepted 31 May 2005
|



