 Back Back
Research Article
ScienceAsia 24 (1998): 037-044 |doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.1998.24.037
INTERACTIONS OF METHYL-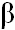 -CYCLODEXTRIN WITH ADENINE AND PYRIDINE/NICOTINAMIDE DERIVATIVES AS DETERMINED BY COMPETITIVE FLUORESCENCE METHODS -CYCLODEXTRIN WITH ADENINE AND PYRIDINE/NICOTINAMIDE DERIVATIVES AS DETERMINED BY COMPETITIVE FLUORESCENCE METHODS
PIAMSOOK PONGSAWASDIa,c AND BRUCE M. ANDERSONb
ABSTRACT: In comparison with 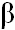 -cyclodextrin, methyl- -cyclodextrin, methyl-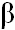 -cyclodextrin was more effective in binding TNS, as indicated by the higher fluorescence intensity enhancement and the higher association constant for the formation of the inclusion compound. Using a competitive fluorescence technique with the dye TNS, adenine and pyridine derivatives were observed to be relatively poor ligands, whereas, N1-alkylnicotinamide chlorides formed inclusion compounds much more effectively with methyl- -cyclodextrin was more effective in binding TNS, as indicated by the higher fluorescence intensity enhancement and the higher association constant for the formation of the inclusion compound. Using a competitive fluorescence technique with the dye TNS, adenine and pyridine derivatives were observed to be relatively poor ligands, whereas, N1-alkylnicotinamide chlorides formed inclusion compounds much more effectively with methyl-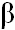 -cyclodextrin. The effectiveness of binding of N1-alkylnicotinamide chlorides increased as a function of the size of the alkyl substituent, with a positive chainlength effect being observed between the N1-heptyl and N1-dodecyl derivatives. The importance of nonpolar interactions in the binding of these derivatives was evident by the observed change in free energy per methylene unit of -0.548 kcal/mole. -cyclodextrin. The effectiveness of binding of N1-alkylnicotinamide chlorides increased as a function of the size of the alkyl substituent, with a positive chainlength effect being observed between the N1-heptyl and N1-dodecyl derivatives. The importance of nonpolar interactions in the binding of these derivatives was evident by the observed change in free energy per methylene unit of -0.548 kcal/mole.
Download PDF
a Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok 10330, Thailand.
b Department of Biochemistry, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, Virginia 24061-0308 U.S.A
c To whom correspondence should be addressed
Received November 30, 1997
|



