 Back Back
Research Article
ScienceAsia 22 (1996): 121-130 |doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.1996.22.121
THE EFFECT OF cryIVB TERMINATOR FRAGMENTS ON EXPRESSION OF THE CHLORAMPHENICOL ACETYL TRANSFERASE GENE IN BACILLUS THURINGIENSIS SUBSP. ISRAELENSIS
NANTAREE SIRICHOTPAKORNa, WATANALAI PANBANGREDa, SOMSAK PANTUWATANAb AND AMARET BHUMIRATANAa
ABSTRACT: A ClaI-BamHI fragment harbouring the terminator region of cryNB gene encoding 130 kDa 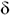 -endotoxin protein from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis was cloned into E. coli cloning vector pGEM7-Zf( +) to allow introduction of useful deletion sites and T7 primer region for sequence analysis. The new recombinant plasmid was designated as pGBT8 which was subjected to further manipulation leading to the construction of thru additional clones. The first clone harboured plasmid pGBT8.1 which contained 221 bp of distal portion of cryNB gene and its terminator. The second clone harboured plasmid pGBT8.2 which contained 127 bp of completed cry/VB terminator. The third clone harboured plasmid pGBT8.3 which contained 86 bp of the cryNB gene or only half of cryNB terminator. All three clones containing various fragments of cryNB terminator were further subcloned into the multicloning sites of pTFM6 vector which located at the position 5' to the cat-86 terminator. Thus, thru double terminators constructs were obtained and designated as pTT1, pTT2, pTT3 respectively. In order to study the effects of single cryNB terminator, a derivative of pTT2 where cat-86 terminator was deleted was constructed and designated as pTT2 -endotoxin protein from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis was cloned into E. coli cloning vector pGEM7-Zf( +) to allow introduction of useful deletion sites and T7 primer region for sequence analysis. The new recombinant plasmid was designated as pGBT8 which was subjected to further manipulation leading to the construction of thru additional clones. The first clone harboured plasmid pGBT8.1 which contained 221 bp of distal portion of cryNB gene and its terminator. The second clone harboured plasmid pGBT8.2 which contained 127 bp of completed cry/VB terminator. The third clone harboured plasmid pGBT8.3 which contained 86 bp of the cryNB gene or only half of cryNB terminator. All three clones containing various fragments of cryNB terminator were further subcloned into the multicloning sites of pTFM6 vector which located at the position 5' to the cat-86 terminator. Thus, thru double terminators constructs were obtained and designated as pTT1, pTT2, pTT3 respectively. In order to study the effects of single cryNB terminator, a derivative of pTT2 where cat-86 terminator was deleted was constructed and designated as pTT2 All the recombinant plasmids were first transformed into Bacillus subtilis MI113 and subsequently transformed into Bacillus thuringiensis c4Q272 using electroporation technique. The presence of cloned terminator regions in the newly constructed plasmids was confirmed by restriction patterns and Southern blot hybridizations. The expression levels of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene (cat) was determined by measuring the specific activity of the enzyme chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT). The cat gene's products were assayed in crude extracts of both B. subtilis MI 113 and B.
thuringiensis subsp. israelensis c4Q272 grown in nutrient broth supplemented with minerals and harvested at the various growth phases, namely, mid log, at the on-set of sporulation (To), and 8 h after on-set of sporulation (T8). By comparing the CAT activities in B. subtilis and B. thuringiensis hosts harbouring various plasmid constructs, it could be concluded that cry/VB terminator had a stimulatory effect on chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene expression in B. thuringiensis subsp. israelensis c4Q272. All the recombinant plasmids were first transformed into Bacillus subtilis MI113 and subsequently transformed into Bacillus thuringiensis c4Q272 using electroporation technique. The presence of cloned terminator regions in the newly constructed plasmids was confirmed by restriction patterns and Southern blot hybridizations. The expression levels of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene (cat) was determined by measuring the specific activity of the enzyme chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT). The cat gene's products were assayed in crude extracts of both B. subtilis MI 113 and B.
thuringiensis subsp. israelensis c4Q272 grown in nutrient broth supplemented with minerals and harvested at the various growth phases, namely, mid log, at the on-set of sporulation (To), and 8 h after on-set of sporulation (T8). By comparing the CAT activities in B. subtilis and B. thuringiensis hosts harbouring various plasmid constructs, it could be concluded that cry/VB terminator had a stimulatory effect on chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene expression in B. thuringiensis subsp. israelensis c4Q272.
Download PDF
a Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Rama VI Road, Bangkok 10400, Thailand.
b Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Rama VI Road, Bangkok 10400, Thailand.
Received May 21, 1996
|

