 Back Back
Research Article
ScienceAsia 22 (1996): 013-020 |doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.1996.22.013
SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS AND PIANTLET REGENERATION FROM OIL PALM (ELAEIS GUINEENSIS JACQ.) CALLUS
WISUT PATCHARAPISUTSIN AND KAMNOON KANCHANAPOOM
ABSTRACT: Callus cultures were initiated from mature embryos of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) on half strength MS (Murashige and Skoog, 1962) medium enriched with either 30 mg/l NAA (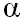 -naphthaleneacetic acid) or 3 mg/l 2,4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid), 3% sucrose and 0.05% (w/v) activated charcoal. Induction of embryogenic, fast-growing calli were obtained when calli were transferred to similar medium with an increase of NAA and 2,4-D to 70 mg/l and 5 mg/l, respectively. These embryogenic calli produced numerous embryoids in these media after several subcultures. Somatic embryo maturation was obtained on medium devoid of NAA or 2,4-D and supplemented with 15% (v/v) coconut water to produce young plantlets. Histological study of embryoids at different stages of development revealed the morphological organization resembled that of zygotic embryo. -naphthaleneacetic acid) or 3 mg/l 2,4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid), 3% sucrose and 0.05% (w/v) activated charcoal. Induction of embryogenic, fast-growing calli were obtained when calli were transferred to similar medium with an increase of NAA and 2,4-D to 70 mg/l and 5 mg/l, respectively. These embryogenic calli produced numerous embryoids in these media after several subcultures. Somatic embryo maturation was obtained on medium devoid of NAA or 2,4-D and supplemented with 15% (v/v) coconut water to produce young plantlets. Histological study of embryoids at different stages of development revealed the morphological organization resembled that of zygotic embryo.
Download PDF
Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Prince of Songkla University, Haad-Yai, Songkla 90112, Thailand.
Received May 8, 1995
|

