 Back Back
Review Article
ScienceAsia 12 (1986): 031-042 |doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.1986.12.031
CHRONIC EFFECT OF TESTOSTERONE AND THYROXINE ON PLASMA AND PITUITARY LEVELS OF LH, FSH, AND PRL IN BLINDED ADULT MALE SYRIAN HAMSTERS.
WANTANEE KAEWPUNNA TRAKULRUNGSI, CHATCHAI TRAKULRUNGSI AND RUSSEL J. REITER
ABSTRACT: This study observed that blinding caused significant suppression of the secretion of the gonadally related adenohypophyseal hormones as well as regression of reproductive organs in the adult male golden hamsters. The pituitary concentrations of FSH and PRL as well as the circulating levels of LH and PRL in the sightless hamsters became significantly less than the corresponding intact control value. Daily administrations of 2 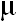 g thyroxine
for 50 days further suppressed significantly both the pituitary and plasma PRL concentrations and the plasma LH level of the bilaterally orbital enucleated male hamsters. No significant changes in the plasma FSH level or in the pituitary concentrations of either LH or FSH of the blinded hamsters were observed 50 days following administrations
with thyroxine alone. Administrations of solely testosterone (1OO g thyroxine
for 50 days further suppressed significantly both the pituitary and plasma PRL concentrations and the plasma LH level of the bilaterally orbital enucleated male hamsters. No significant changes in the plasma FSH level or in the pituitary concentrations of either LH or FSH of the blinded hamsters were observed 50 days following administrations
with thyroxine alone. Administrations of solely testosterone (1OO 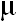 g, every other day) or of combined testosterone and thyroxine to the blinded male hamsters caused significant
suppressions on the pituitary concentration of LH but had no significant effects on either the pituitary PRL or FSH concentration. While plasma PRL and FSH levels were not significantly affected, the plasma LH level of the sightless male hamsters treated with either testosterone or combined testosterone and thyroxine was markedly suppressed below the vehicles-injected blind control level. Regarding the effect of hormone administrations on the reproductive organ weights of the blinded hamsters, it was observed that marked suppressions on the testes weights of the sightless hamsters were produced by administrations with testosterone, thyroxine, or the combined hormone treatments; and that the decline in testes weights paralleled closely the decline in plasma LH and PRL levels. While injections of thyroxine alone produced no significant change in the weight of the seminal vesicles and the coagulating glands, the weight of these accessory sex organs increased significantly above the blind control level following testosterone or combined testosterone and thyroxine treatments. Nevertheless, the weights of the accessory sex organs in the testosterone or testosterone and thyroxine treated groups, whose circulating levels of LH and PRL remain significantly depressed below intact control levels, were significantly less than the weight of these organs in the intact controls. All these results
suggest that the pineal of the sightless hamster does not directly exert its effects on gonadal g, every other day) or of combined testosterone and thyroxine to the blinded male hamsters caused significant
suppressions on the pituitary concentration of LH but had no significant effects on either the pituitary PRL or FSH concentration. While plasma PRL and FSH levels were not significantly affected, the plasma LH level of the sightless male hamsters treated with either testosterone or combined testosterone and thyroxine was markedly suppressed below the vehicles-injected blind control level. Regarding the effect of hormone administrations on the reproductive organ weights of the blinded hamsters, it was observed that marked suppressions on the testes weights of the sightless hamsters were produced by administrations with testosterone, thyroxine, or the combined hormone treatments; and that the decline in testes weights paralleled closely the decline in plasma LH and PRL levels. While injections of thyroxine alone produced no significant change in the weight of the seminal vesicles and the coagulating glands, the weight of these accessory sex organs increased significantly above the blind control level following testosterone or combined testosterone and thyroxine treatments. Nevertheless, the weights of the accessory sex organs in the testosterone or testosterone and thyroxine treated groups, whose circulating levels of LH and PRL remain significantly depressed below intact control levels, were significantly less than the weight of these organs in the intact controls. All these results
suggest that the pineal of the sightless hamster does not directly exert its effects on gonadal
Download PDF
a Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Science. Mahidol University, Rama VI Road, Bangkok 10400, Thailand.
Department of Cellular and Structural Biology, The University of Texas, Health Science
Center at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX 78284, USA
Received 8 April 1985
|

