 Back Back
Research Article
ScienceAsia 7 (1981): 147-153 |doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.1981.07.147
CALCULATIONS OF LONG-WAVE
SPECTRAL ATMOSPHERIC EMISSIVITIES
AND POTENTIAL OF SELECTIVE RADIATION COOLING FOR CHIANGMAI. THAILAND
P. BOON-LONG
ABSTRACT: Long-wave spectral emissivities for the climate of Chiang Mai, thailand, were computed, with emphasis on emissivity in the 8-13 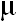 m transparency window. Calculations
were based on 1970 monthly- averaged upper-air data up to a height of 10 km, assuming clear skies. Outward radiation fluxes from several surfaces at ground level at Chiang Mai were also estimated. Results show that between 8-13 m transparency window. Calculations
were based on 1970 monthly- averaged upper-air data up to a height of 10 km, assuming clear skies. Outward radiation fluxes from several surfaces at ground level at Chiang Mai were also estimated. Results show that between 8-13 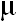 m, atmospheric emissivity varies from 0.42 in January and February to 0.81 in June and July. At other wavelengths, the emissivity is essentially unity. Hemispherical total emissivity ranges
from 0.77 in February to 0.87 in June and July. Outward radiation fluxes from an ideal cooling surface varies from 50 W/m2 in January to 20 W/m2 in July. Potential application of this outward radiation flux in a passive cooling system is discussed. m, atmospheric emissivity varies from 0.42 in January and February to 0.81 in June and July. At other wavelengths, the emissivity is essentially unity. Hemispherical total emissivity ranges
from 0.77 in February to 0.87 in June and July. Outward radiation fluxes from an ideal cooling surface varies from 50 W/m2 in January to 20 W/m2 in July. Potential application of this outward radiation flux in a passive cooling system is discussed.
Download PDF
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand.
Received 5 November 1981
|

