 Back Back
Research Article
ScienceAsia 32 (2006): 279-284 |doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2006.32.279
Chemical and Physical Properties of Flour Extracted
from Taro Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott Grown in
Different Regions of Thailand
Jirarat Tattiyakul,* Sukruedee Asavasaksakul and Pasawadee Pradipasena
ABSTRACT: Chemical and physical properties of taro Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott flour extracted from
different-sized taro corms cultivated in 4 different regions of Thailand were investigated. Taro chips were
composed of 84.6 – 91.5 g carbohydrates/100 g flour, 5.1 – 8.7 g protein/100 g flour, 1.1-3.2 g fiber/100 g
flour, 2.0 – 5.0 g ash/100 g flour, 0.4 – 0.9 g fat/100 g flour, and 317.0 – 435.8 mg calcium oxalate /100 g
flour. The carbohydrate content of taro was not affected by corm size, but by cultivating location. An
extraction using 0.05% (w/v) sodium hydroxide yielded purified taro flour (PTF) with lower protein content,
compared with the water extraction method. PTF contained 96.9 – 98.2 g carbohydrates/100 g flour, 0.7 –
1.9 g protein/100 g flour, 0.1 – 0.3 g fat/100 g flour, 0.1 – 0.9 g fiber/100 g flour, 0.1 – 0.4 g ash/100 g flour,
and 182.0 – 200.1 mg calcium oxalate /100 g flour. All PTFs had 18.8 – 22.4 % amylose, with an average
degree of polymerization of 195 – 238. The starch granules were small and polygonal, with an average
diameter of 1.3 – 2.2 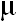 m. With an A-type crystalline structure, PTF had a low swelling power of 11.0 – 17.4
g/g dry flour and low solubility of 0.081 – 0.132 g/g dry flour at 80oC. The pasting temperature and peak
viscosity of PTF were 78 – 87 oC, and 264 – 441 RVU, respectively. m. With an A-type crystalline structure, PTF had a low swelling power of 11.0 – 17.4
g/g dry flour and low solubility of 0.081 – 0.132 g/g dry flour at 80oC. The pasting temperature and peak
viscosity of PTF were 78 – 87 oC, and 264 – 441 RVU, respectively.
Download PDF
Department of Food Technology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Payathai Road,
Patumwan, Bangkok 10330, Thailand.
* Corresponding author, E-mail: Jirarat.t@chula.ac.th
Received 28 Nov 2005,
Accepted 15 Feb 2006
|

