 Back Back
Research Article
ScienceAsia 30 (2004): 327-334 |doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2004.30.327
Synthesis and Characterization of
Poly(L-lactide-co-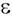 -caprolactone) Copolymers: -caprolactone) Copolymers:
Effects of Stannous Octoate Initiator and
Diethylene Glycol Coinitiator Concentrations
Yodthong Baimark and Robert Molloy*
ABSTRACT: A series of approximately 50:50 mol % poly(L-lactide-co-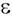 -caprolactone) copolymers were synthesized
by bulk copolymerization of L-lactide (LL) and -caprolactone) copolymers were synthesized
by bulk copolymerization of L-lactide (LL) and 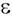 -caprolactone (CL) using stannous octoate (Sn(Oct)2) and
diethylene glycol (DEG) as the initiating system. The resulting P(LL-co-CL) copolymers were characterized
by various analytical techniques including dilute-solution viscometry, GPC, 1H/13C NMR and DSC. It was
found that both the Sn(Oct)2 and DEG concentrations exerted important but different effects on the molecular
weight (average and distribution), chain microstructure and temperature transitions of the copolymer
formed. Whereas the Sn(Oct)2 initiator mainly affected the molecular weight distribution and comonomer
sequencing, the DEG coinitiator was more influential on the average molecular weight. The results are
discussed in the light of current theories of the coordination-insertion mechanism of cyclic ester ringopening
polymerization. -caprolactone (CL) using stannous octoate (Sn(Oct)2) and
diethylene glycol (DEG) as the initiating system. The resulting P(LL-co-CL) copolymers were characterized
by various analytical techniques including dilute-solution viscometry, GPC, 1H/13C NMR and DSC. It was
found that both the Sn(Oct)2 and DEG concentrations exerted important but different effects on the molecular
weight (average and distribution), chain microstructure and temperature transitions of the copolymer
formed. Whereas the Sn(Oct)2 initiator mainly affected the molecular weight distribution and comonomer
sequencing, the DEG coinitiator was more influential on the average molecular weight. The results are
discussed in the light of current theories of the coordination-insertion mechanism of cyclic ester ringopening
polymerization.
Download PDF
Biomedical Polymers Technology Unit, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Chiang Mai
University, Chiang Mai 50200, Thailand.
* Corresponding author, E-mail: robert@chiangmai.ac.th
Received 29 Apr 2004,
Accepted 27 Aug 2004
|



