 Back Back
Research Article
ScienceAsia 14 (1988): 263-276 |doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.1988.14.263
A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF [3H]-PARA-AMINOCLONIDINE BINDING TO
RENAL TISSUES OF HYPERTENSIVE AND NORMOTENSIVE RATS
BUNGORN SRIPANIDKULCHAI* AND J.M. WYSS
ABSTRACT: A specific agonist for 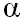 2-adrenoceptor, [3H]-para-aminoclonidine [3H]-PAC),
was used to characterize 2-adrenoceptor, [3H]-para-aminoclonidine [3H]-PAC),
was used to characterize 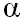 2-adrenoceptor binding in renal membranes from spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) and normotensive Wistar-Kyoto rat (WKY). The results from saturation and kinetic analyses revealed that two distinct binding sites, with relative high and low affinities, exist in the kidneys of both SHR and WKY. The Kd values for both binding sites were the same in SHR and WYK. However, the maximum, receptor density (Bmax) of both binding sites were higher in SHR than in WKY (32 2-adrenoceptor binding in renal membranes from spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) and normotensive Wistar-Kyoto rat (WKY). The results from saturation and kinetic analyses revealed that two distinct binding sites, with relative high and low affinities, exist in the kidneys of both SHR and WKY. The Kd values for both binding sites were the same in SHR and WYK. However, the maximum, receptor density (Bmax) of both binding sites were higher in SHR than in WKY (32  5.3 versus 22 5.3 versus 22  1.2 and 116 1.2 and 116  12.5 versus 65 12.5 versus 65  2.0 fmol/mg protein for the high- and the low-affinity binding sites, respectively). GTP affected [3H]-PAC binding to renal membranes from both SHR and WKY similarly and in a concentration-related manner. On the other hand, NaCI inhibited [3H]-PAC binding to the low-affinity binding site to a lesser extent than to the high-affinity binding site in WKY, but both binding sites of SHR were similarly inhibited by NaCI. An increase in the receptor density of the renal membranes from SHR correlated well with their renal norepinephrine level and mean systolic blood pressure. Therefore, the data presented herein indicate that the alteration of [3H]-PAC binding to 2.0 fmol/mg protein for the high- and the low-affinity binding sites, respectively). GTP affected [3H]-PAC binding to renal membranes from both SHR and WKY similarly and in a concentration-related manner. On the other hand, NaCI inhibited [3H]-PAC binding to the low-affinity binding site to a lesser extent than to the high-affinity binding site in WKY, but both binding sites of SHR were similarly inhibited by NaCI. An increase in the receptor density of the renal membranes from SHR correlated well with their renal norepinephrine level and mean systolic blood pressure. Therefore, the data presented herein indicate that the alteration of [3H]-PAC binding to 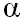 2-adrenoceptor of the rat kidney is related to hypertension 2-adrenoceptor of the rat kidney is related to hypertension
Download PDF
Department of Cell biology and Anatomy, Univiversity of Alabama at Birmingham,
Birmingham, Alabama 35294, U.S.A.
Received 1 May 1988
|

